Wire Gauge Chart UK
Complete Guide to the Wire Gauge Chart UK: Understanding Sizes & Uses
Choosing the right cable thickness is essential for safety, performance, and compliance with electrical standards. If you’re working on a DIY project, automotive repair, or professional electrical installation, understanding the wire gauge chart UK can help you select the appropriate wire size quickly and confidently. This guide explains how UK wire sizing works, how it differs from other systems, and how to read a gauge chart effectively.
What Is a Wire Gauge Chart (UK)?
A wire gauge chart UK lists the thickness of electrical cables commonly used in the United Kingdom. Unlike the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system, the UK mainly uses metric measurements, such as the cross-sectional area of the conductor in square millimetres (mm²). This metric approach makes it easy to understand the cable’s current-carrying capacity and suitability for different applications.
Why the UK Uses Metric Wire Sizes Instead of AWG
The UK electrical system follows BS 7671 (IET Wiring Regulations), which specifies cable sizes in mm². Here’s why:
- Clearer measurement: mm² directly relates to conductor size.
- Standardised safety ratings: easier to match cable size with circuit breakers and fuses.
- European compatibility: most EU/UK wiring uses metric sizing for uniformity.
Because of this, the UK wire gauge chart is not identical to American charts, though approximate equivalents can be made.
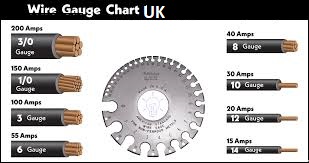
Common Wire Sizes in the UK (with Approximate AWG Equivalents)
Below is a simplified wire gauge chart UK overview showing typical UK cable sizes and their rough AWG comparisons. (Note: AWG conversions are approximate and not exact equivalents.)
| UK Size (mm²) | Approx. AWG | Typical Use in the UK |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 mm² | ~20 AWG | Low-power lighting, electronics |
| 0.75 mm² | ~18 AWG | Lamps, small appliances |
| 1.0 mm² | ~17 AWG | Lighting circuits |
| 1.5 mm² | ~15 AWG | Lighting and small load circuits |
| 2.5 mm² | ~13 AWG | Socket outlets, ring circuits |
| 4.0 mm² | ~11 AWG | High-power appliances, cookers (some circuits) |
| 6.0 mm² | ~9 AWG | Electric showers, cookers |
| 10 mm² | ~7 AWG | Main feeds, high-load circuits |
| 16 mm² | ~5 AWG | Consumer unit tails, large loads |
This table helps when comparing tools or products that list AWG sizes but are being used within a UK electrical setup.
How to Read a Wire Gauge Chart UK Correctly
When using a wire gauge chart UK, focus on three main factors:
1. Cross-Sectional Area (mm²)
This determines how much current the cable can safely carry.
2. Insulation Type
Different insulation materials—such as PVC, rubber, or heat-resistant compounds—affect the maximum allowable current.
3. Application
Cables for lighting, ring circuits, and high-powered appliances all require different sizes based on load and safety standards.
Benefits of Using a Wire Gauge Chart in the UK
- Improved safety by preventing overheating or electrical faults
- Accurate matching of cable sizes to circuit protection devices
- Compliance with UK electrical regulations
- Better performance for both household and industrial electrical systems
Summary
Understanding the wire gauge chart UK is essential for anyone selecting the right cable for electrical work. Because the UK uses metric sizing, it’s clearer and more reliable than systems based purely on gauge numbers. By learning how to interpret wire sizes in mm², you can ensure your installations remain safe, compliant, and efficient.
Here is a unique, clear, and helpful FAQ section that naturally includes your keyword “wire gauge chart UK” where appropriate.
FAQ: Wire Gauge Chart UK
1. What is a wire gauge chart UK used for?
A wire gauge chart UK helps you compare different wire sizes based on their cross-sectional area in millimetres (mm²). It is used to choose the correct cable thickness for electrical installations, ensuring safety and compliance with UK wiring regulations.
2. Does the UK use AWG sizes?
Not typically. The UK mainly uses mm² measurements, not American Wire Gauge (AWG). However, the wire gauge chart UK often includes approximate AWG conversions for people working with imported tools or components.
3. How do I know which wire size I need?
Choose the wire size based on:
- The current your device or circuit requires
- The insulation type
- The distance of the cable run
- UK wiring regulations (BS 7671)
A wire gauge chart UK can guide you, but always follow official safety standards.
4. Is 2.5 mm² cable the standard for UK sockets?
Yes, 2.5 mm² cable is commonly used for socket ring circuits in UK homes. It is one of the most referenced sizes in a typical wire gauge chart UK.
5. Can I convert mm² to AWG?
Yes, but conversions are approximate because the systems are based on different measurement methods. A wire gauge chart UK that includes AWG comparisons can give you a rough match, but it’s not exact.
6. What wire size is used for lighting in the UK?
Most UK lighting circuits use 1.0 mm² or 1.5 mm² cable. These sizes appear clearly in most UK cable charts.
7. Why does wire size matter?
Choosing the correct wire size prevents overheating, voltage drop, and potential electrical faults. The wire gauge chart UK helps ensure your cable is suitable for the load.
8. Where can I find a reliable wire gauge chart UK?
You can find charts in:
- Electrical textbooks
- BS 7671 guidance materials
- Professional electrical supplier websites
- DIY and home improvement platforms




